Introduction to Alzheimer’s disease
Simple introduction
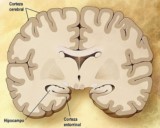
Alzheimer, commonly known as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), senile dementia, is a neurodegenerative disease with a slow onset and worsening over time. This disease accounts for 60% to 70% of the causes of dementia. A common early symptom is loss of short-term memory.
Cause
The true cause of Alzheimer’s disease is still unknown. Alzheimer’s disease is currently regarded as a neurodegenerative disease, and nearly 70% of the risk factors are believed to be related to genetics; other risk factors include head trauma, depression and high blood pressure.
But the development of Alzheimer’s disease is associated with the deposition of fibrillar amyloid plaques (amyloid beta) and Tau protein in the brain. Amyloid beta can clump together and become plaques in the brain, which can be harmful to brain cells in patients with abnormal amyloid buildup in the brain.
Lethality to human health
Alzheimer’s disease is the main cause of dementia. People with dementia suffer from impairment of memory, thinking or decision-making skills, interfering with daily activities. As far as the current human medical technology is concerned, once a patient discovers Alzheimer’s disease, the symptoms will only increase with age and there is no possibility of recovery.
How important is it?
Alzheimer’s is the only major disease yet to be conquered, and is the leading cause of dementia, the seventh leading cause of death in the world.
How big is the market
Some 850,000 Britons and 5.8 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, the leading cause of dementia in which people with dementia experience impairment of memory, thinking or decision-making, interfering with daily activities. The American Alzheimer’s Association announced that there are 6.5 million Alzheimer’s patients and their families in the United States, and it is expected to increase to 15 million by 2050.
Japan’s Alzheimer’s Association International pointed out that there are currently 50 million Alzheimer’s patients worldwide, and the number may increase to 150 million by 2050.
It is estimated that there are about 210,000 Alzheimer’s patients in China, and the prevalence rate is 9.59 times that of 1990.
An April study by the UK’s Office for National Statistics (ONS) revealed that dementia and Alzheimer’s disease are the leading causes of death in the UK by 2022, accounting for 65,967 deaths.
In 2015, the World Health Organization announced that approximately 29.8 million people worldwide suffer from Alzheimer’s disease. WHO predicts 150 million people will be demented by 2050
My book about Alzheimer
In my recent book, “The Rules of 10 Baggers” I discuss the development of Alzheimer’s disease and related companies:
- Sections 3-4, page 141
Drugs currently on the market
How many drugs are there?
So far, the FDA has only approved seven:
- Four cholinesterase inhibitors
- AbbVie’s NMDA receptor (N-methyl-D-aspartate)
- Biogen and Eisai get two accelerated approvals
Another is likely to be approved:
- Donanemab monoclonal antibody developed by Eli Lilly
List of famous Alzheimer drugs
The FDA has only reviewed 7 drugs so far. See Table 1 for details. The second half of this article discusses the most popular new generation monoclonal antibodies and RNA therapy drugs in recent years, which have been approved or will be approved by the FDA.
| Scientific name | Vendor | Drug type | Side effects |
| Galantamine | Johnson & Johnson | Cholinesterase inhibitors | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and loss of appetite |
| Rivastigmine | Novartis | Cholinesterase inhibitors | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and loss of appetite |
| Donepezil | Pfizer | Cholinesterase inhibitors | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and loss of appetite |
| NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) | AbbVie | Inhibits the toxin effect of calcium ions on brain neurons Antagonist used | Hallucinations, confusion, dizziness, headache, fatigue, etc. |
| Donepezil Hydrochloride | AbbVie | It exerts a therapeutic effect by enhancing the function of cholinergic nerves | Heart palpitations, diarrhea, insomnia, vomiting, muscle cramps, fatigue, lethargy and loss of appetite |
| Aducanumab | Biogen and Eisai | monoclonal antibody | The incidence of brain swelling is 12.6%, and the bleeding rate is 17.3% |
| Lecanemab | Biogen and Eisai | monoclonal antibody | Brain swelling and bleeding in the brain, called amyloid-related imaging abnormality (ARIA) |
| Donanemab | Eli Lilly | monoclonal antibody | ARIA, the incidence of severe ARIA is still 1.6% |
| ALN-APP gene silencing therapy | Alnylam | RNA interference blocks protein production | Side effects are very mild |
FDA accelerated approval
The FDA has given accelerated approval for two drugs that may slow the progression of AD and are only indicated for people with mild disease:
- Lecanemab (Lequembi®)
- Aducanumab (Aduhelm®)
These drugs target removal of brain amyloid, one of the proteins that build up in brain in people with AD. Before starting these drugs, your doctor will need to confirm the presence of amyloid in your brain. Your doctor will order either an amyloid PET scan or spinal tap.
The effects of lecanemab and aducanumab in people with early AD are still being studied.
Aduhelm
Biogen (ticker: BIIB) has been approved by the FDA in 2021. Aduhelm, a new drug for Alzheimer’s disease with a one-year drug price set at US$56,000 per person, is full of controversy. It is the first approved new drug for Alzheimer’s disease in nearly two decades. After the launch, the rate of clinicians prescribing the drug is surprisingly low ;according to FactSet (ticker: FDS), sales in the first quarter after being approved to go public were only $300,000, far short of the estimated $12 million. Many well-known leading hospitals refused to adopt it, influential professional medical committees also voted to reject the efficacy of the drug, and medical insurance companies are also waiting for the coverage conditions issued by Medicare before making a decision on whether to enroll.
However, Biogen and its Japanese partner Eisai received FDA approval for the new Alzheimer’s drug Aduhelm on June 7, 2021, but encountered doubts about the safety of the drug from the medical community and the market. The House Oversight and Reform Committee, as well as the Energy and Commerce Committee, issued a report on the FDA’s review, pricing and marketing of Aduhelm, stating that the process was “rife with non-compliant behavior” and that contacts with pharmaceutical companies prior to the review, Did not comply with FDA’s internal guidelines and practices, raised eight doubts.
Aducanumab, initially priced at $56,000 a year, is not covered by insurance companies and has been rejected by regulators in many countries.
Lecanemab
In July 2022, Biogen (ticker: BIIB) and Eisai formally applied to the FDA for accelerated approval of Lecanemab. The FDA can expedite approval of a drug to bring it to market quickly based on the promise of a drug that could help patients with a serious disease more effectively than existing medicines. The US Federal Food and Drug Administration (FDA) accelerated the approval on January 6, 2023, a new drug for Alzheimer’s disease, Lecanemab (Lencanezumab), and the trade name is Leqembi.
Although Lecanemab also has the risk of brain swelling and hemorrhage in treatment, according to the results of clinical trials published in November last year, FDA still found that Lecanemab slowed down the cognition of patients with mild impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease to a certain extent. Declining capacity, accelerated approval of Lecanemab.
Efficacy of Lecanemab’s new drug: “Moderate” delays the disease, not a cure Lecanemab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the amyloid protein accumulated in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients. Amyloid-beta-binding action on hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease Lecanemab is the latest treatment to target the underlying disease process affecting Alzheimer’s disease, rather than just treating the symptoms of the disease. If these trials confirm that the drug has clinical benefit. The antibody is injected intravenously every two weeks at a dose of 10 mg per kilogram based on the patient’s weight.
The most common adverse events in the lecanemab group were reactions to the intravenous infusion and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) abnormalities, such as brain swelling and cerebral hemorrhage, known as amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA). May be life-threatening.
Lecanemab costs about $26,500 a year and works almost as well as donanemab.
In August 2023, Japan officially approved Lecanemab to be launched in Japan. This is the first drug for Alzheimer’s disease in Japan.
Non-accelerated approval
Why rejected by FDA?
The FDA rejected Eli Lilly’s request due to the limited number of patients who had seen at least 12 months of drug exposure in a clinical study, according to the company.
Donanemab
On May 3, 2023, the latest clinical data released by Eli Lilly (ticker: LLY) showed that Donanemab monoclonal antibody has the potential to surpass Lecanemab; donanemab is an antibody whose target is a protein “β-amyloid Protein”. In the clinical results, the efficacy of Donanemab seems to be more dominant. Proven to clear abnormal amyloids from the brain. Donanemab needs to be given several times a month.
According to Lilly, this is the first time an Alzheimer’s drug has slowed cognitive decline by more than 35% in a Phase 3 trial. Indeed, purely from the numbers, Donanemab is better than Lecanemab. Phase III results showed that after 18 months of treatment, the CDR-SB score of the lecanemab group was 27% lower than that of the stabilizer group.
Eli Lilly has applied to the FDA for approval. If approved, it will follow Biogen (ticker: BIIB) and Eisai to formally apply to the FDA for Lecanemab, which was recently approved by the FDA, and Aduhelm, the third drug proven to delay Alzheimer’s disease.
Although most of the side effects in the Donanemab treatment group were mild to moderate and resolved or stabilized after appropriate treatment, amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) were the most concerned adverse reactions of the drug. The incidence of severe ARIA was still 1.6%. Two of these patients even died from ARIA, and one died after severe ARIA.
RNA interference
At present, the new Alzheimer’s disease drugs Donanemab and Lecanemab have been proven to clear the abnormal amyloid protein in the brain. Alnylam’s ALN-APP treatment goes a step further by reducing the protein that causes Alzheimer’s disease, preventing its production in the first place. Medical research by British neurologist Catherine Mummery, who led the trial, found that a single dose of ALN-APP “gene silencing” therapy reduced levels of the dangerous amyloid precursor protein 90%, and still 65% lower after six months.
Instead of clearing the protein, the therapy stops its production upstream in the first place. If you just remove the proteins that are already there, you have to keep removing the damage while the valve is still open, but if you close the valve, you have a better chance of preventing further damage.
Phase 1 trials presented at a conference in Amsterdam last month showed the treatment was safe, with minimal side effects. Injected directly from the spinal cord in the lower back, it only needs to be administered once or twice a year.
Influence
Cost
Due to the astonishing investment cost and time of drug manufacturers, and the difficulty of development, the prices of the only three major drugs currently on the market are very high.
Side effect
It is worth noting that not only the cost, but also the three new drugs have very dangerous side effects.
Impact on the capital market
Related stocks performance
| Tick | 10/16/2023 share price | Stock performance in past 1 year | P/E | Market value (in US$ billion) | Dividend yield |
| LLY | 617.57 | 85.46% | 85.8 | 586.26 | 0.73% |
| BIIB | 265.82 | -1.38% | 14.47 | 38.48 | 0.00% |
| ESAIY | 13.9 | -10.41% | 47.95 | 16.92 | 0.00% |
| JNJ | 157.9 | -5.25% | 32 | 380.23 | 3.01% |
| PFE | 33.69 | -22.82% | 8.98 | 190.07 | 4.87% |
| NVS | 96.74 | 32.30% | 26.96 | 218.34 | 3.62% |
| ABBV | 148.03 | 2.51% | 30.45 | 261.28 | 4.00% |
| ALMN | 166.91 | -14.44% | 0 | 20.86 | 0.00% |
| S&P 500 | 4,371.98 | 18.87% | 18.52 | 35,002 | 1.80% |
Eli Lilly
On May 3, 2023, Eli Lilly announced the clinical data of Donanemab, the stock price rose by 6.68%, and the market value exceeded 400 billion U.S. dollars, becoming a well-deserved big brother in the field of pure pharmaceutical companies. For a super giant like Eli Lilly, it is rare to see sharp fluctuations in market value. In the past three years, it is extremely rare for Lilly to fluctuate by more than 5% in a single day, but Donanemab has triggered three of them.
Biogen
As I described in my book “The Rules of 10 Baggers“, Alzheimer’s disease is the only major human disease that has yet to be overcome. Almost all large drug companies have invested heavily in research and development, but most of them have not. After success, only Roche (ticker: RHHBY), Biogen and Eli Lilly, two large pharmaceutical companies, have made progress.
In particular, Biogen has repeatedly released a variety of drugs for Alzheimer’s disease. The company’s stock price has fluctuated greatly in the past few years, and it has almost fluctuated violently with the progress of the main stage clinical results of the company’s Alzheimer’s disease drugs.
Divided health insurers
Some private insurance companies are reluctant to pay patients for the first approved new Alzheimer’s disease drug because the new drug, although experimental, costs as much as 26,000 yuan a year. Medicare, commonly known as the red and blue card, provides Leqembi benefits for most patients. Insurers refusing to provide benefits for Leqembi include Highmark Insurance, which launched Blue Cross Blue Shield Insurance (BCBS) in New York, Pennsylvania, Delaware, and West Virginia; Blue Cross Blue Shield of North Carolina; Independence BC in the Pennsylvania area.
I am the author of the original text, the essence of this article was originally published in Smart Magzine
Relative articles
- “Alzheimer, the only major disease yet to be conquered, current progress and related companies“
- “Gilead, lord of antiviral drug, reveals world’s first AIDS vaccine“
- “Viking is developing two future star new drugs at the same time“
- “FDA approved first ever MASH drug“
- “Walking helps thinking, get you recharged and refeshed“
- “Why Eli Lilly become global pharmaceutical market value king?“
- “UnitedHealthcare, the world’s largest health insurer, role model of Dow Jones“
- “Eli Lilly, a big pharma with astonishing valuation“
- “Novo Nordisk’s new diabetes drug Semaglutide,Ozempic,Wegovy and Mounjaro found to have surprising weight-loss effects“
- “Big pharma spin-offs, and advantages to invest them“
- “The next No. 1 pharmaceutical leader AbbVie“
- “Stable Dow Component Merck, how does it make money?“
- “Roche, the king of anti-cancer“
- “Abbott, the world’s most important medical device and nutritional food supplier, how does it make money?“
- “Pfizer, the world’s largest pharmaceutical company“
- “Inventors are rarely successful, but improvers are successful and profitable“
- “Roche, the king of anti-cancer“
Disclaimer
- The content of this site is the author’s personal opinions and is for reference only. I am not responsible for the correctness, opinions, and immediacy of the content and information of the article. Readers must make their own judgments.
- I shall not be liable for any damages or other legal liabilities for the direct or indirect losses caused by the readers’ direct or indirect reliance on and reference to the information on this site, or all the responsibilities arising therefrom, as a result of any investment behavior.